Data/python
[stochastic] python을 활용한 백테스팅
노는토요일
2022. 7. 3. 16:32
스토캐스틱 Trading
스토캐스틱 트레이딩에서 참고해야할 지표는 크게 3개이다.
Fast %K
# 함수 정의
# Fast %K ((현재가 - n기간 중 최저가)/(n기간 중 최고가 - n 기간 중 최저가)) * 100
def get_stochastic_fast_k(close_price, low, high, n =5):
fast_k = (close_price - low.rolling(window=n).min())/(high.rolling(window=n).max()
- low.rolling(window=n).min())*100
return fast_k
Slow %K(Fast %D)
# Slow %K = Fast %K의 m기간 이동평균(SMA) = # Fast % D
def get_stochastic_slow_k(fast_k, n=3):
slow_k = fast_k.rolling(window=n).mean()
return slow_kSlow %D
# Slow %D = Slow %K의 t기간 이동평균(SMA)
def get_stochastic_slow_d(slow_k, n=3):
slow_d = slow_k.rolling(window=n).mean()
return slow_d위의 3가지를 참고해 트레이딩을 진행하는데, Fast %k 가 가장 급변하는 변화를 잘 잡아내고, Slow %D가 2번의 이동평균화를 거치다 보니 조금더 완만하게 변화를 잡아낸다.
어떤 전략을 쓸지는 투자자의 판다에 딸라 달라집니다. 필자의 경우 주가의 급등락을 빠르게 잡아내고 싶어서 Fast %k를 활용해 트레이딩을 적용해 보았습니다.
Trade BackTesting
Fast % k 80이상 매도 20이하 매수
###################################
## Fast %K 80이상 매도 20이하 매수 ##
#####################################
###############
## 삼성 전자 ##
###############
#데이터 로드
raw_df=fdr.DataReader('005930','2022-01-01').reset_index()
# seriese 정의
high_ = raw_df.High
low_ = raw_df.Low
close_ = raw_df.Close
raw_df['fast_k'] = get_stochastic_fast_k(close_,low_,high_)
fast_k = raw_df['fast_k']
raw_df['slow_k'] = get_stochastic_slow_k(fast_k)
slow_k = raw_df['slow_k']
raw_df['slow_d'] = get_stochastic_slow_d(slow_k)
slow_d = raw_df['slow_d']
buy_idx = np.where(raw_df['fast_k']<=20)[0]
sell_idx =np.where(raw_df['fast_k']>=80)[0]
# 이전 action이 buy였으면 공란
for k in range(len(raw_df)):
if k in buy_idx:
raw_df.loc[k,'action'] = 'buy'
elif k in sell_idx:
raw_df.loc[k,'action'] = 'sell'
else:
raw_df.loc[k,'action'] = ''
rst_df = raw_df.copy()
for k in range(len(rst_df)):
if k ==0:
continue
if rst_df.loc[k-1,'action'] =='buy': # 이전 시점에 buy면 holding ## action
rst_df.loc[k,'action'] = 'holding'
elif rst_df.loc[k-1,'action'] =='sell': # 이전 시점에 sell이면 sell_holding ## action
rst_df.loc[k,'action'] = 'sell_holding'
elif (rst_df.loc[k-1,'action'] =='sell_holding') and(rst_df.loc[k,'action'] =='buy') : # 이전시점이 sell_hlidng면서 현재 buy러 바뀌면 넘기기
continue # 포지션 바뀌는 경우
elif (rst_df.loc[k-1,'action'] =='holding') and(rst_df.loc[k,'action'] =='sell') : # 포지션 바뀌는 경우
continue
elif rst_df.loc[k-1,'action'] =='sell_holding': # 이전이 sell_holding 이이고 다음도 같으면 포지션 유지 # position stay
rst_df.loc[k,'action'] = 'sell_holding'
elif rst_df.loc[k-1,'action'] =='holding': # 이전이 holding 이고 다음도 같으면 포지션 유지 # position stay
rst_df.loc[k,'action'] = 'holding'
else:
continue
rst_dfDate/Open/High/Low/Close/Volume/Change/fast_k/slow_k/slow_d/action/
| 2022-01-03 | 79400 | 79800 | 78200 | 78600 | 13502112 | 0.003831 | NaN | NaN | NaN | |
| 2022-01-04 | 78800 | 79200 | 78300 | 78700 | 12427416 | 0.001272 | NaN | NaN | NaN | |
| 2022-01-05 | 78800 | 79000 | 76400 | 77400 | 25470640 | -0.016518 | NaN | NaN | NaN | |
| 2022-01-06 | 76700 | 77600 | 76600 | 76900 | 12931954 | -0.006460 | NaN | NaN | NaN | |
| 2022-01-07 | 78100 | 78400 | 77400 | 78300 | 15163757 | 0.018205 | 55.882353 | NaN | NaN | |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2022-06-15 | 61300 | 61500 | 60200 | 60700 | 26811224 | -0.019386 | 10.000000 | 9.130435 | 7.753623 | holding |
| 2022-06-16 | 61300 | 61800 | 60500 | 60900 | 23394895 | 0.003295 | 16.666667 | 14.685990 | 9.871176 | holding |
| 2022-06-17 | 59400 | 59900 | 59400 | 59800 | 29053450 | -0.018062 | 11.764706 | 12.810458 | 12.208961 | holding |
| 2022-06-20 | 59800 | 59900 | 58100 | 58700 | 34111306 | -0.018395 | 14.634146 | 14.355173 | 13.950540 | holding |
| 2022-06-21 | 58700 | 59200 | 58200 | 58500 | 24902181 | -0.003407 | 10.810811 | 12.403221 | 13.189617 | holding |
114 rows × 11 columns
Trade history 조회
df_sample = rst_df.copy()
df_sample['range'] = df_sample['High']-df_sample['Low']
df_sample[df_sample['action'].isin(['buy','sell'])]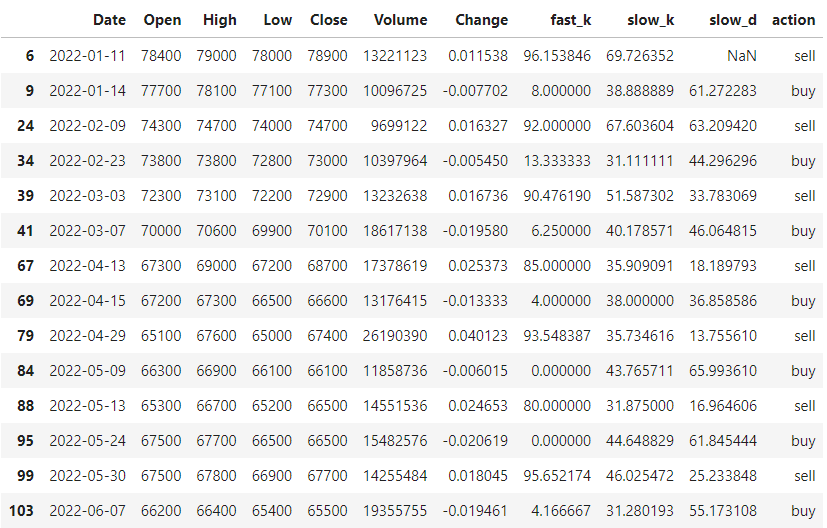
수익률 계산
def get_profit(df):
final_df = df[df['action'].isin(['buy','sell'])]
final_df = final_df.reset_index(drop=True)
trading_cnt = final_df.shape[0]
profit = []
buy_lst = []
for idx in range(len(final_df)):
# 매수 action이 들어올 경우 매수
if final_df.action[idx] =='buy':
buy_price = final_df.Close[idx]
buy_lst.append(buy_price)
# 첫 action이 매도인 경우
elif idx == 0 and final_df.action[idx] =='sell':
continue
#그 외의 경우 정상 매도
else:
sell_price = final_df.Close[idx]
profit.append(-(buy_price) + sell_price) # 음수가 되어야함.
# 1 buy_pirce > sell_preice 인경우 비싸게 싸서 싸게 판경우 즉 손실
# 2 buy_pirce < sell_preice 인 경우 싸게사서 비싸게 판경우 그래서 이득
profit_sum = np.sum(profit)
average_buying = np.mean(buy_lst) # 매수 평단가
profit_percentage = round(profit_sum/average_buying,2)
profit_num = len(profit)
return trading_cnt,profit_sum,profit_num,profit_percentage
삼성전자 6개월간 Fast%k 기반 수익률
get_profit(rst_df) # Fast% K 트레이딩 14회 , 한 주당 수익 : -1700원, 이익횟수 : 6번, 수익률 -2%